Analysis of the innovative experience of a preschool educational organization
Competition between educational organizations leads to the fact that recently it has become relevant to involve preschool educational organizations (hereinafter referred to as PEOs) in innovative activities, support social and educational initiatives at all levels of education systems (city, federal), promote innovative experience, innovative products (innovations). ), allowing to improve the education system.
The content of the innovative activities of preschool educational institutions is determined by the priority areas of the preschool educational institutions development program.
The need for innovation arises when there is a need to solve a problem, a contradiction is created between the desire and the actual result.
Each teaching staff has the right to innovative activities. But in this case, he must take on certain obligations in preparing and organizing the innovation, since children become the object of any pedagogical initiative.
An analysis of the concept of “innovation activity” in the dictionary defines it as an activity (including financial, scientific, commercial, technological, organizational) that is aimed at implementing innovative projects and creating an innovative infrastructure.
In pedagogy, this is purposeful pedagogical activity aimed at obtaining new knowledge, introducing new pedagogical technologies into the educational process, and gaining new pedagogical experience.
Innovative activities in education imply changing and updating the entire pedagogical process, introducing new formations into the traditional system.
To analyze the innovative experience of our preschool educational institution, we will consider the innovative experience of an esthete teacher.
At the beginning, a problem was identified: there was not enough demonstration and interactive material when introducing children to the fine arts.
The purpose of the innovation: to provide support for children’s familiarization with fine arts using ICT.
Classification of innovation (in the field of management, didactics, psychology, private methodology, interdisciplinary field, etc.): private methodology.
The innovation has gone through the following stages: idea formation, goal setting, development, mastery at the stage of experimental research, dissemination. Within the framework of the order of the kindergarten, kindergartens of the ANO DO “Planet of Childhood “Lada”, all-Russian competitions, website.
The innovation has undergone expert testing: many times.
The innovative experiment went through the following stages: ascertaining, formative, control.
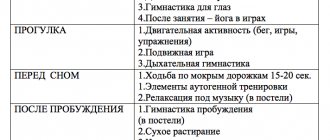
Stater:
— insufficient multimedia equipment;
- multimedia presentations on the artistic and aesthetic direction on the Internet do not correspond to the objectives of the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard and the general education program of the kindergarten, and the age characteristics of children;
— children do not have the skills to watch educational films and multimedia presentations;
— the skill of working with an interactive whiteboard has not been developed.
Formative:
— acquisition of additional interactive equipment in order to solve the problems of the Federal State Educational Standard;
— selection of material, illustrations, scientific and educational films;
— creating multimedia presentations, cutting educational films in accordance with age;
— developing children’s skills in working with an interactive whiteboard and multimedia presentations;
— creation and testing of notes on educational activities, artistic and aesthetic development with the inclusion of interactive games and multimedia presentations.
Control:
— inclusion of interactive equipment at 100%;
— increasing children’s interest and activity in watching multimedia games and working with an interactive whiteboard by 50%;
— conducting control classes with children;
— familiarization of colleagues with the experience of working within the kindergarten, kindergartens of the ANO DO “Planet of Childhood “Lada”, various competitions.
Obstacles to development and implementation:
— there is not enough illustration of a single format;
— not all kindergarten groups have the necessary equipment.
Expert control was carried out by: specialists of the kindergarten, kindergartens of the ANO DO “Planet of Childhood “Lada”, participation in all-Russian competitions, self-control.
Special notes on the significance of innovation and its assessment taking into account alternative opinions: the innovative activity of an esthete teacher makes it possible to use an effective system for working with multimedia presentations when working with children. The introduction of an innovative methodological product into practice makes it possible to ensure positive dynamics of educational results in the development of pupils and preschool educational institutions as a whole.
Ivanushkina Valentina Mikhailovna,senior teacher of kindergarten No. 114 of JSC Russian Railways
Relevance and prospects of experience. Its significance for improving the educational process.
Currently, the entire general education system is being modernized in the direction of forming a developed, socially oriented personality, capable of adapting to the difficult socio-economic conditions of society and ready for their creative transformation. Updating the content of education consists of bringing it into line with modern trends in the development of science, social orders, as well as the need to increase the general cultural level of the younger generation. The priority task of education is to create optimal conditions for the development of creativity both in the educational system as a whole and in each of its subjects.
Ivan Bunin wrote: “A kindergarten is a garden where children’s souls blossom.” The talents and creativity hidden in every person can be compared to the seeds hidden in a person, which either grow and subsequently bear fruit, or wither and die. Everything depends on the soil in which they are sown, that is, on the cultural, social environment in which the child was born and continues to grow and develop. Only an intelligent, competent, creative teacher can reveal a child’s soul.
The primary goal of an educational institution, both at the federal level and at JSC Russian Railways, is the development of an active, intellectually developed, extraordinary creative personality with the ability to behave non-standardly. To achieve this goal, effective technologies are used to develop imagination, literacy and other basic abilities of children, which requires highly qualified teachers who are the direct organizers of the educational process in the institution. The teacher is the organizing principle in the formation and development of the personality of each child, and his competence and personal qualities are the decisive condition for the success of innovative transformations of educational institutions of JSC Russian Railways. To get the best results in working with children, it is necessary to maximize the development of the innovative potential of each teacher.
The personnel policy of the non-state preschool educational institution "Kindergarten No. 114 of JSC Russian Railways", aimed at developing the innovative potential of teachers, is carried out on the basis of dialogue interaction and consists of developing professional competence and creating conditions for the manifestation of creative activity of teachers.
Conditions for the formation of the leading idea of experience.
An analysis of studies related to innovation processes in education indicates a sustained interest in studying various aspects of the innovative activities of educational organizations. At the same time, there are practically no works devoted to the study of the problems of developing the innovative potential of the teaching staff.
The effectiveness of developing the innovative potential of the teaching staff will be achieved if it is purposefully developed and the preparedness of teachers to implement innovations is improved. The purpose of the work: to create in a preschool institution the necessary psychological, pedagogical and organizational and pedagogical conditions for the effective development of the innovative potential of each teacher.
In accordance with the goal, specific tasks were identified:
- identify the essence of the teacher’s innovative potential;
- analyze the level of innovation potential of the team;
- determine methods and forms of developing the innovative potential of a preschool teacher;
- to develop a system of methodological work for the kindergarten to develop the innovative potential of the teaching staff.
Theoretical basis of experience.
The innovative potential of a teacher is a set of professional, sociocultural and creative characteristics of an individual, expressing the teacher’s readiness to improve professional activities and the presence of internal means and methods that ensure this readiness. This is the desire and opportunity to develop one’s interests and ideas, to look for one’s own unconventional solutions to emerging problems, to perceive and creatively implement existing non-standard approaches in education, to implement innovative ideas, projects and technologies, to prove oneself as a researcher and developer.
The essence of the innovative potential of the teaching staff lies in its ability to self-development and implement innovative ideas, projects and technologies. The system of indicators of innovative potential includes: the receptivity and attitude of teachers to innovations, their preparedness to master innovations, the level of innovation of teachers in the school team, the level of creative activity of teachers, the development of their communication connections.
Technology of experience. Contents, methods, teaching techniques.
In order to identify the level of innovative potential, a set of questionnaires for teachers was developed and tested (Appendices 1,2).
The following types of competence have been identified as the basic components of the general professional competence of preschool teachers:
- normative and methodological competence;
- personal-humanistic competence;
- design and research competence;
- information and communication competence.
The engine for developing innovative potential is motivation. The innovative activity of a teacher is socially motivated, but it is also stimulated by personal external and procedural-substantive motives, and is determined by many needs (from physiological to the need for self-actualization). The development of the innovative potential of teaching staff is achieved through the use of such forms of interaction with teachers that will contribute to the disclosure of their internal capabilities.
For each type of professional competence, the forms and methods of working with personnel were determined:
- normative and methodological competence: seminars using active teaching methods, master classes;
- personal-humanistic competence: trainings, psychological and pedagogical lectures;
- design and research competence: implementation of projects, creative laboratories, organization of experimental work;
- information and communication competence: long-term workshop “Comp and I”.
Seminars and workshops remain the most effective form of methodological work in kindergarten; every teacher here is an active participant in communication. The seminar not only increases the level of knowledge and skills, but also encourages teachers to take initiative, a creative approach and an active position in their activities. Teachers gain experience in communication skills, group discussions and public speaking; depending on the phase of the seminar, each teacher takes either the position of a speaker, or an understander, or a critic.
The master class involves demonstrating teaching abilities, general culture, competence, education, pedagogical and methodological literacy. Its main goal is the transfer of pedagogical experience, work systems, and author’s findings. The master class consists of two parts: ½ - demonstration of work with children; ½ - work with teachers in order to convey teaching experience. It is important to skillfully demonstrate work with children and discuss the results obtained with colleagues.
The formation of personal-humanistic competence is facilitated by training - a form of group work that teaches how to work with life situations. During the training, a group of teachers has a triple impact on each group member:
- cognitive – a group member realizes how his usual behavior and ways of relating allow him to resolve situations, comprehends the reasons for his behavior and understands how to behave more effectively in similar situations in the future;
- emotional – the training participant, supported by other members of the group, realizes his psychological defense mechanisms, adjusts relationships with others, changes his emotional attitude towards himself, and, as a result, his self-esteem increases and self-esteem stabilizes;
- behavioral – a group member develops adequate situations and methods of behavior.
Seminars, master classes, and trainings become effective forms of working with teachers when using active teaching methods. Active learning methods teach you to gain new knowledge and experience not by passively recording the information received, but in the course of stable and continuous mental activity, relying on your own experience and interaction with colleagues. At the same time, the motives that are used to encourage teachers to be active are professional interest, creativity, a competitive gaming approach and various types of emotional influence.
In the non-state preschool educational institution "Kindergarten No. 114 of JSC Russian Railways", active methods for developing innovative potential have been tested, such as: problem-based method (brainstorming, case method, discussion), business game, project. The significance of these innovative methods was the formation of a new culture of thinking, ensuring the implementation of creative transformation processes.
The general scheme of problem methods is as follows: a problem situation is described, then a search for a solution is organized, then the optimal ones are selected.
One of the most productive methods of activating collective creative activity is “Brainstorming”. This method is based on the free expression by participants of a variety of ideas that can help resolve the problem.
Brainstorming is carried out in several stages:
Stage 1 - generating ways to solve the problem, when the storming participant proposes his own option, still at the idea level. The time limit for each idea is 1-2 minutes, no evidence is required. All ideas are logged or recorded on tape. At this stage, any criticism is prohibited, including hidden criticism in the form of skeptical smiles, gestures, and facial expressions. The total number of proposals should not exceed approximately half the number of participants. The more ideas, the better! Even if these are absurd ideas.
Stage 2 - searching for arguments in support of the proposed solutions. Based on the number of ideas recorded, several small groups are created, and ideas are distributed between the groups by drawing lots; Then, within 8-10 minutes, each group develops as many arguments as possible in favor of the idea it has received, even if the participants do not really like the method of solution.
Stage 3 - selection of the most reasoned solutions. The leader of each group presents the arguments developed by the group, and then a discussion begins with the goal of selecting approximately half of the available options for further development.
Stage 4 - criticism of the selected solutions. From the cards with ideas, those that did not pass the previous stage are removed. And then again in group work (similar to the second stage) there is sharp, but evidence-based criticism of the given option.
Stage 5 - selection of the most productive solution methods, for which there were the fewest critical judgments according to the methodology of the third stage.
To activate the process of generating ideas during the “assault”, techniques such as inversion (do the opposite), analogy (do as it was done in another solution), empathy (consider yourself part of the task, find out your feelings, sensations) are used. , fantasy (do something fantastic).
As a result of the discussion, a solution to the problem is found (but it will be wrong if it is the only one - it is advisable to have two or three options). Teachers need to get used to understanding the plurality of truths, the admissibility and naturalness of divergent paths to the same result.
The case study method—analysis of specific situations—is effective in working with personnel. The case presents a description of a specific situation (“photograph of reality”) that requires practical resolution.
The peculiarity and attractiveness of the case method is that it allows you to simulate a real problem that you may have to face in practice. Cases develop analytical, research, communication skills, develop the ability to analyze a situation, plan a strategy and make management decisions. Teachers, working with the situation, learn to correctly set tasks, identify key factors, and justify their positions and decisions.
Types of cases: situation-problem, situation-assessment, situation-illustration, situation-anticipation. Cases can be presented in a variety of forms, from a few sentences on one page to many pages. A case may contain a description of one event in one group or the history of the development of a kindergarten over many years. Cases can be presented in a variety of forms: printed, video, audio, etc.
Example: a case study of the structure of a kindergarten and its place in society is presented for discussion at the seminar “Kindergarten is an open developing system.”
Scheme for using the “case study” method in working with teachers:
- Preparatory stage (before the seminar): teachers are tasked with getting to know the situation, understanding the essence of the matter - the main problematic issues, and mentally formulating their behavior strategy in the upcoming discussion.
- Work in small creative groups (4-5 people): in which the first discussion of the situation and collective solution of the assigned tasks take place.
- Work in a large group (all small groups gather together) takes place in the form of a discussion (1.5-2 hours). Representatives of small groups argue their positions. A rational assessment of various situations is given, and on this basis - the development of a common collective decision, taking into account alternatives.
One of the methods of group interaction is discussion (from the Latin discussio - consideration, research) - discussion of any controversial issue or problem. This method ensures the active involvement of teachers in the search for truth, creates conditions for them to openly express their thoughts, positions, attitudes towards the topic under discussion and has a special ability to influence the attitudes of its participants in the process of group interaction. As a unique technology, the discussion itself includes methods such as “Brainstorming” and the case method.
The developmental function of discussion is associated with stimulating students’ creativity, developing their ability to analyze information and provide reasoned, logically constructed evidence of their ideas and views, increasing students’ communicative activity, and their emotional involvement in the educational process. Techniques for activating teachers:
- Leading teachers to a contradiction and then finding a way to resolve it.
- Colliding contradictions in practical activities.
- Presentation of different points of view on the same issue.
- Consideration of the phenomenon from various positions, for example, the teacher, the head of the kindergarten, parents, etc.
- Comparison, generalization, comparison of facts, conclusions from the situation.
- Posing specific questions for generalization, justification, specification, logic of reasoning.
As a variation, for well-trained teachers who know how to work creatively, a theatrical discussion is used. The discussion begins with the “leading theorist” presenting his theory. Then questions are formulated both by the theorist himself and by “opponents”, which will allow consolidation of knowledge. Success depends on everyone’s willingness to cooperate, on the ability to compare different value systems and conduct dialogue. In the discussion “History of Fine Arts”, each of the participants became for some time a representative of a particular movement of painting, a bearer of certain artistic values and an exponent of them in the process of dialogue. He developed his own attitude both to “his” theory and to other schools. The point of the “dialogue of theorists” is to evaluate the contribution of each theory to artistic culture.
Business games are an effective way to “cultivate” the innovative culture of teachers. By definition, a game is a type of activity in situations aimed at recreating and assimilating social experience in which self-control of behavior is formed and improved. A business game is a form of recreating the objective and social content of professional activity, modeling such systems of relationships that are characteristic of this activity as a whole.
Designing a business game includes three stages: preparation, implementation, analysis and generalization. With the help of symbolic means (language, speech, graphs, tables, documents) in a business game, a professional environment is reproduced, similar in its main essential characteristics to the real one. At the same time, in a business game only typical, generalized situations are reproduced in a compressed time scale. For example, a parent meeting can be played out in one game session, and the development of a development program for a preschool institution can be played out in up to three.
When working with preschool teachers, various modifications of business games are used: simulation, operational, role-playing, etc. Imitation games simulate the activities of a teacher, child, group, their specific activity and setting, the conditions in which an event occurs or an activity is carried out. Operational games help to practice specific specific operations, for example, drawing techniques. In role-playing games, tactics of behavior, actions, and the performance of functions and responsibilities of specific individuals are practiced. To conduct these games, a model play of the situation is developed, and roles with mandatory content are distributed among teachers. For example, educator, conflict initiator, defenders.
The dictates of the times necessitate the acquisition of design and research competence. The teacher is an agent of change in education and works in conditions of change: an increase in the volume of scientific, methodological and research components in the structure of pedagogical activity, he is actively involved in innovative activities in education, in the process of creating new models of teaching practice and in their scientific understanding.
Important in the development of innovative potential is the formation of a teacher’s ability to carry out project activities, when it is necessary not only to express an idea, one’s own way of solving a problem, but to present it in the form of a fully developed plan (project) and be able to assess its competitiveness. In addition, if a teacher or preschool specialist is trained in design technology, then he will use this technology when working with children, and only when such training is organized is truly collaborative learning possible.
Types of projects:
- Research - completely subordinated to the logic of research and have a structure that approximates or completely coincides with genuine scientific research.
- Creative - do not have a detailed structure of joint activities, they are subject to the genre of the final result (newspaper, video, holiday, etc.), but the design of the results of the project requires a clear, well-thought-out structure in the form of a script for a film, a holiday, the design of newspaper sections, an album, etc. P.
- Informational - aimed at collecting information about some object or phenomenon.
- Socially significant - they are distinguished by the result of the activities of its participants that is clearly defined from the very beginning, which is necessarily focused on the social interests of the project participants themselves or any group of people.
Most of the design (collecting information, analysis, conducting research, examination, etc.) is carried out by teachers for quite a long time. Some socially oriented projects are becoming more important for the entire preschool institution as a whole (such as the release of a preschool educational institution booklet; the preparation of newspaper pages; the design of sociological research).
The design and research competence of a teacher can be defined as the ability and readiness of an individual to independently and effectively carry out research activities, predict its results and apply them in practice. Involving the maximum number of teachers in research activities is possible when organizing experimental work.
Performance Analysis
Various forms and methods of developing the innovative potential of teachers (brainstorming, case method, discussion, etc.) were introduced into the methodological work. Seminars held in kindergarten have become of great educational value.
Experimental activities on the topic “Pedagogical model of artistic and aesthetic education in kindergarten” were intensified. As a result of the joint work of kindergarten teachers and teachers of the Mordovian Republican Institute of Education, a diagnostic program for artistic and aesthetic education of preschoolers was created and developed, a model of artistic and aesthetic education for preschoolers was built based on a combination of different types of arts and independent creative activity of children.
Educators and specialists tested methods that stimulate the development of children's creativity, introduced integrated classes, and a new form of leisure activity - the Salon. At the Literary Salon, children get acquainted with the work of poets and writers, read poetry, play rhyming games, etc. The Art Salon organizes meetings with painters and graphic artists, and opens Vernissages of the work of young artists. Classical music is played in the Music Salon. The integrated forms of the Salons (literature and music, painting and theater...) are very interesting and meaningful. In the cozy and formal atmosphere of the Salon, preschoolers not only get acquainted with art, but also learn good manners. Result: disclosure of artistic, poetic, artistic talents; bringing closer and strengthening mutual understanding between children and adults.
As a result of experimental work on artistic and aesthetic education in a preschool institution, not only a new system of working with children, but also of the teaching staff as a whole was built. Positive results of work with gifted children and clubs were noted. The kindergarten's experience in artistic and aesthetic education of preschoolers has been summarized, and a methodological manual has been published in a circulation of 250 copies.
Preschool teachers have mastered various computer programs and information and communication technologies. They are used in the educational process, to prepare documentation, and use Internet resources in the process of self-education, dissemination of their experience, and communication with parents of students through virtual topics. The use of ICT has made it possible to modernize the educational process, increased its efficiency, motivated children to search activities, and differentiated learning taking into account the individual characteristics of children.
The list of tasks that the institution’s website solves is wide:
- advertising, informing the public and parents about the kindergarten;
- consulting on various issues of upbringing and education of preschoolers;
- communication with the teacher at a time convenient for parents and the teacher himself (option “Forum”, “Question-answer”, “Announcements”);
- dissemination of the experience of the preschool institution as a whole and of individual teachers.
Teachers and specialists working in the non-state preschool educational institution “Kindergarten No. 114 of JSC Russian Railways” are enthusiastic and creative people, ready for serious research work, development of original programs, modern pedagogical technologies that allow improving the educational process, leaders, dreamers and improvisers.
Visual application
Annex 1
Questionnaire “Teachers’ receptivity to new things”
Do you constantly monitor advanced pedagogical experience in your activities, strive to implement it taking into account the changing educational needs of society and the individual style of your teaching activity?
- Are you constantly educating yourself?
- Do you adhere to certain pedagogical ideas and develop them in the process of teaching?
- Do you collaborate with scientific consultants?
- Do you see the prospects for your activities and predict them?
- Are you open to new things?
Rating scale: always – 3 points, sometimes – 2 points, never – 1 point.
Determining the level of receptivity of the teaching staff to innovations: K = Kfact: Kmax,
where Kfact is the actual number of points received by all teachers; Kmax – the maximum possible number of points.
K < 0.45 - critical level; 0.45 < K < 0.65 – low level; 0.65 < K < 0.85 - acceptable level; K > 0.85 is the optimal level.
Appendix 2
Questionnaire “Motivational readiness of the teaching staff to master innovations”
If you are interested in innovation, applying innovations, then what motivates you to do this? Please select up to three answers.
- Awareness of the inadequacy of the results achieved and the desire to improve them.
- High level of professional aspirations, strong need to achieve high results.
- The need for contacts with interesting, creative people.
- The desire to create a good, effective education for children.
- The need for novelty, renewal, change of scenery, overcoming routine.
- Need for leadership.
- The need for search, research, better understanding of patterns.
- The need for self-expression, self-improvement.
- A feeling of one’s own readiness to participate in innovative processes, self-confidence.
- The desire to test in practice the acquired knowledge about innovations.
- The need for risk, overcoming routine.
- Material reasons: salary increase, opportunity to pass certification, etc.
- The desire to be noticed and appreciated.
Result: the stronger the motives associated with the possibility of personal self-realization prevail among teachers, the higher the level of innovative potential of the teaching staff.
Appendix 3
An example of developing the innovative potential of teachers at the seminar “Kindergarten - an open developing system”
Target:
- include preschool teachers in the search for a solution to the problem of developing a kindergarten as an open developing system;
- activate the innovative potential of teachers using active forms and methods of teaching;
- learn to communicate, conduct a discussion, develop a common opinion in microgroups;
- identify innovative technologies and methods for working with children, parents, and society.
The first lesson of the seminar was devoted to considering the level of development of a preschool institution at this stage. A case study of the structure of a kindergarten and its place in society was presented, after which microgroups worked on a diagram of this structure and the subsequent development of the institution.
At the second lesson of the seminar, the development of a socially significant project “Kindergarten - an open developing system” was started, a scheme for the development of the institution was outlined (agreements with social institutions for childhood, publishing activities, joint events). The development of the project continued in groups between seminar sessions.
The purpose of the design: to identify the most significant problems for the staff of a preschool institution and try to solve these problems using design technology.
Tasks:
- identify the problem that needs resolution
- determine ways to solve the problem
- distribute roles in the group, responsibility
- submit the result for evaluation
- analyze the results obtained and your own actions, arrange them in the form of diagrams and text
At the third lesson, teachers were divided into microgroups, which each began working in their own area: one of them developed a detailed plan for a year of work with social institutions of childhood, another - a strategy for publishing activities, a third - a plan for PR activities, and a fourth - interaction with families. The work of the microgroups continued after the lesson, discussed and adjusted.
In the fourth lesson - summing up the work of small groups, defending the submitted works, defining evaluation criteria and rating assessment.
The fifth lesson was devoted to the use of ICT for the development of a preschool institution. Teachers presented options for using information and communication technologies to implement the project “Kindergarten - an open developing system”: presentations of a preschool institution, groups, work in certain areas (by personal choice), options for proposed sites, Web pages, etc.
The education system makes new demands on the upbringing and training of the younger generation, the introduction of new approaches that should contribute not to replacing traditional methods, but to expanding their capabilities, including by means of computer technology.
To plan for increasing the information and communication competence of teachers, the didactic role and place of information and communication technologies in the educational process, the possibility of using ICT tools by teachers were determined, and in accordance with them, a system of methodological work was built.
The optimal components of information and communication competence of teachers were selected:
- the use of ICT for the training and development of preschool children;
- creating your own multimedia products (photo and video presentations, slide films);
- registration of monitoring results of the educational process (Microsoft Office Excel, Microsoft Office Word)
- creating your portfolio;
- use of digital technologies in photography, photo editing (Adobe Photoshop, Helen's Eyes part, etc.)
- use of Internet resources.
MAGAZINE Preschooler.RF
Experience of innovative activities in the work of the preschool educational institution “Biology for preschool children”Prepared by: senior teacher of MBDOU d/s No. 7 - Zaitseva T.B.
“The whole huge world around me, above me and below me, is full of unknown secrets. I will discover them all my life, because this is the most exciting activity in the world.” V. Bianchi
Modern progress is moving forward with great strides. The state began to pay great attention to fundamental sciences, actively involved education in their development, and preschool childhood did not remain on the sidelines. Of course, preschool children will not discover new chemical elements, and will not yet create a spaceship, but their inquisitive and pure mind is able to assimilate the structure of plants and humans, and their liberated imagination will build unprecedented landscapes, grow new fruits, and miracles - dream birds - will soar into the sky...
The first encounters with science occur in childhood. Based on knowledge about the capabilities and characteristics of preschool children, our kindergarten teachers introduce children to the wonderful science of biology. Why did this seemingly complex science interest the teaching staff? There are several reasons for this.
First, let's look at the definition of science. Biology is a system of sciences whose objects of study are living beings and their interaction with the environment. Biology is the study of all aspects of life, particularly the structure, functioning, growth, origin, evolution and distribution of living organisms on Earth.
Plants, animals, and even man himself are always before the eyes of a child and cannot help but interest him. This means that objects of flora and fauna are very convenient for viewing and studying.
Secondly, these sciences will guide children into the world of health, help them gain valeological knowledge: acquire the right habits, teach them how to care for their body, observe hygiene and nutrition rules, and join sports.
Thirdly, correctly selected forms of work with preschoolers will help them master basic natural science knowledge in biology, which underlies medicine, agriculture, ecology, i.e. become a little explorers and naturalists.
The preschool education program does not provide for an introduction to the concept of “biology ,” but in their work, preschool institutions introduce children to the structure and significance of plants and animals for human life. This happens in classes on cognitive development, life safety and ecology. With the introduction of in-depth work to obtain primary knowledge in biology, preschoolers become more familiar with the world of plants and animals of various natural zones of our planet, the microcosm of biological objects, and become familiar with the history of the origin of life on Earth. This knowledge helps to cultivate a caring attitude towards natural resources, to understand the essence of many phenomena occurring before their eyes.
The goal of the work was to create an effective system for the early inclusion of preschool children in scientific activities to form initial scientific ideas in biology.
In order for this activity to be successful, preliminary work has been carried out:
- available methodological and material resources are systematized
- opportunities for improving conditions for organizing innovative activities have been identified
- interaction with partners (preschool institutions of the district, local history museum, children's library) was organized.
Immersing a preschool child into the world of biology has become a difficult but interesting task for teachers. For a preschool institution, this direction became innovative; the entire kindergarten staff immersed itself in the work.
Innovation activities are based on the principles:
- scientific character
- realism and accessibility
- value attitude towards natural objects, life and health
- entertaining.
In order to improve the conditions for the formation of primary scientific knowledge of preschoolers in biology, corporate training of teaching staff (consultations, a quiz, a methodological week and open viewings of educational activities) was carried out at preschool educational institutions; methodological materials were developed (didactic games, booklets, “flip books” , illustrative material , riddles, descriptive stories, media presentations, lapbooks).
To improve the subject-development environment, each group created models of “Natural Zones” : “Forest” , “North” , “Hot Countries” , “Nature of the Far East” , “Meadow” , “Village” , “Underwater World” . The use of three-dimensional compositions made it possible to conduct didactic games, simulate stories and game situations, which clearly show the need for each component of the natural and plant world for life on Earth.
In order for the work to proceed evenly, a creative group of teachers developed long-term planning of educational activities and a cycle of classes for children of senior preschool age, which made it possible to gradually introduce children to plants and animals, and the structure of man.
When implementing innovative activities, the leading method was game-based problem-based learning. It permeated the content of every lesson and conversation. Considering that the proposed activities are designed for preschool children, gaming motivation has acquired an entertaining nature, aimed at solving cognitive problems. Each preschooler was given the opportunity to learn a lot of new things in the course of their leading activity - play. It is in it that he can organically imagine himself as a researcher, a discoverer of the secrets of nature.
The combination of classical (visual, verbal, practical) and modern problem-based game methods was aimed at creating the most favorable conditions for the formation of sustainable cognitive interest in the study of biological objects.
Speaking about the world of plants and animals, teachers paid attention to representatives of the flora and fauna that are located directly next to the pupil. One of the advantages of the locality of the village in which our preschool is located is its proximity to nature. How can you miss such a wonderful opportunity?!
In order to see moss, sea buckthorn, rose hips, honeysuckle, you don’t have to go far - many of these plants are located within the kindergarten. Just stretch out your hand and in your palm you will already find wonderful wild plants full of vitamins. In conversations and classes, students learned why they are useful, and which plants are dangerous for humans and why.
Outside of class, children became acquainted with the world of animals on excursions to the reserve and museum. The guides talked about where the musk deer lives, about the habits of the lynx and the wolf. During the games, the children compared animals from hot countries and inhabitants of the Far Eastern taiga, brown and polar bears.
The early inclusion of a child in scientific activities in biology was helped by the use of synthesized forms of interaction with peers and adults, studying one’s body, the structure of animals and plants during experimental, research and work activities. Situations were simulated for the child in which they had to put forward hypotheses, make assumptions, reason and, most importantly, get a positive or negative result.
Separately, it is necessary to highlight experimental activities as part of the search and research method. Experimentation is an effective method of understanding the patterns and phenomena of the surrounding world. The main advantage of children's experimentation is that it gives children real ideas about the various aspects of the object being studied, about its relationships with other objects and the environment. When forming the primary ideas of a preschool child about biological objects, practical activities were carried out on growing plants (houseplants, peas, beans), studying their structure and growth characteristics. Work in nature and environmental games became assistants in this.
One of the most vivid impressions of the guys was working with a microscope. Examining a drop of water, milk, animal hair, or human hair at multiple magnification, the children observed the essence of things, admired and rejoiced at the discoveries.
The combination of methods and techniques used, systematic work, and the use of various forms of interaction made it possible to achieve positive results in developing children’s interest in the flora and fauna, and developing healthy lifestyle habits in children.
The presented classes, entertainment and experimental activities were carried out in groups. Teachers presented one of the classes at open screenings during the Days of Professional Excellence, which traditionally take place in a preschool institution. The content of the direct educational activities exceeded the program framework, but each teacher tried to show interesting methodological findings that would help preschool children in a playful way to learn a lot of new things about plants and animals on our planet, the structure of man, and his physical capabilities.
The early inclusion of preschoolers in the world of biology has become part of the work of the Municipal Innovation Complex of the Verkhnebureinsky District. As part of mutual visits by preschoolers to the open events area of the Municipal Innovation Platform, the entertainment “Meet Your Body” . It was visited by pupils from preschool institutions in the area.
Upon completion of the work done, a video magazine “I want to know everything!” , which is posted on the website of the preschool institution http: //mbdou-ds7-rodnichok. lbihost. ru/, where you can find all the materials on creating an effective system for the early inclusion of preschool children in scientific activities to form initial scientific ideas in biology.
Participation in innovative activities allowed the preschool institution to function in development mode, to grow with each child, when the main goal is not acquiring new knowledge, but interestingly living every day of the most valuable period of a person’s life - CHILDHOOD.
| Next > |
The use of innovative forms, methods, technologies in working with preschool children
The use of innovative forms, methods, technologies in working with preschool children
The process of reorganizing the entire education system places high demands on the organization of preschool education and training, and intensifies the search for new, more effective psychological and pedagogical approaches to this process.
The development of preschool education and its transition to a new qualitative level cannot be carried out without the development of innovative forms, methods, means and innovative technologies.
Innovative activity of a teacher
is a necessary part of the educational process. The introduction of innovations means the need for educators to adapt their activities to changing conditions and use non-standard techniques in educational processes. The work of a teacher should not be limited to exclusively old and proven methods; some variety is necessary.
In the modern understanding, innovation is “the manifestation of new forms or elements of something, as well as a newly formed form or element.” A synonym for innovation is the concept of “innovation”.
The innovative activity of the teacher is
to begin mastering developmental innovations, to introduce new forms, methods, techniques, tools, technologies, programs into the educational process. Apply and study in practice, use your personal experience and knowledge.
The purpose of using innovation is
to create a person-oriented educational environment in preschool educational institutions, allowing to create conditions for full physical, spiritual, psycho-emotional health, interpersonal, group developmental interaction of children, parents, teachers and specialists.
Tasks:
to cultivate the social and personal qualities of preschoolers who can think outside the box and creatively;
develop initiative, curiosity, volition, the ability for creative self-expression, stimulate communicative, cognitive, play and other activity of children in various types of activities;
to develop children’s skills in using modern innovative technologies aimed at the successful socialization of the individual in society and increasing the level of intellectual thinking and creative imagination.
Any technology has means that motivate, activate, and shape the activities of students. In some technologies, these means constitute the main idea and basis for the effectiveness of the results. Such technologies include gaming technologies.
Play is the leading activity
, all preschool age. The developmental potential of the game lies in its very nature. The pedagogical value of the game lies in the fact that it becomes the strongest motivational factor; the child is guided by personal attitudes and motives.