Developmental education in kindergarten as a means of intellectual education of preschoolers
Bibliographic description:
Guzenko, T.V. Developmental education in kindergarten as a means of intellectual education of preschoolers / T.V. Guzenko, O.V. Melgunova, O.V. Mukhina. — Text: direct // Questions of preschool pedagogy. — 2022. — No. 2 (39). - pp. 14-16. — URL: https://moluch.ru/th/1/archive/189/5967/ (access date: 02/05/2022).
The technology of developmental education in kindergarten is substantiated, containing goals, objectives, and methodological approaches. A model has been developed describing the stages, methods and means of intellectual education of preschool children. The leading role of educational games for the development of the personality of a preschooler has been proven.
Key words: developmental education; preschoolers; intellectual education; preschool educational organization.
Introduction. In the modern world, where the key role of development is based on the intensive deterministic implementation of scientific and technological progress, early socialization and general development of the child’s personality takes place, the effect of which is enhanced by the informatization of social relations and the digitalization of education, it is important to pay the greatest attention to spiritual and moral values.
In this regard, there is a need to once again address the problem of introducing fundamental issues of the theory and practice of developmental education into the educational process of kindergarten. What will this give to the kindergarten? Firstly, it will promote the development of cognitive processes, educate intellectually, form communicative and health-preserving competencies, and develop emotional intelligence.
Developmental education was first introduced into pedagogy by V.V. Davydov to designate a limited range of processes and phenomena.
The main theories of developmental education for younger schoolchildren include the didactic theory of L. V. Zankov and the theory of meaningful generalization and formation of educational activity by D. B. Elkonin, co-authored with V. V. Davydov.
A. Yu. Yaretskaya developed the program “Developmental game in the activities of preschoolers,” which has proven its effectiveness. The author has developed a set of pedagogical conditions for the implementation of educational game technology that promotes the intellectual education of preschool children [1].
L. S. Vygotsky developed the theory and practice of the problem of learning and development, comparing the influence of various types of learning on the course of child development.
The concepts of intelligence and intellectual education of preschool children have been widely studied by foreign scientists (L. Lévy-Bruhl, M. Wertheimer, W. Köhler, J. Piaget, K. Duncker, J. Brunner, H. Eysenck, G. Gardner, R. Sternberg, K Fischer, R. Feuerstein, E. Hunt, etc.).
Domestic researchers L. S. Vygotsky, N. V. Bordovskaya, S. L. Rubinshtein, A. R. Luria, P. Ya. Galperin, B. G. Ananyev, L. A. Venger, Yu. N. Emelyanov, A. K. Markova, R. S. Nemov, I. P. Podlasy, I. Stepanova, B. M. Velichkovsky, M. A. Kholodnaya, and others developed and improved the content and concepts of intelligence. As a result, scientists came to the conclusion that developmental education has a great influence on intellectual education.
The study of scientific literature made it possible to formulate the purpose of the study - what is the role of developmental education in kindergarten in the intellectual education of preschoolers.
The object of the study is the intellectual education of preschool children in kindergarten.
The subject of the research is developmental education as a means of intellectual education of preschool children in preschool settings.
Research objectives:
1) Develop a model of developmental education, the implementation of which is aimed at the intellectual education of preschoolers.
2) Develop developmental educational events and games in preschool educational institutions.
3) Create pedagogical conditions for the implementation of the developmental education model.
Research methods and subjects
The study has been taking place at the Child Development Center - Kindergarten No. 162 in the city of Voronezh since 2022. Study participants: preschoolers of different age groups; educators; additional education teachers; educational psychologist; musical director. The implementation process is controlled by the deputy head of the preschool educational institution and a senior teacher.
Research methods: intellectual games; educational events; educational activities during the implementation of the main educational program; public events (holidays, competitions, Olympics, etc.)
Results and its discussion
The model of intellectual education of preschool children through developmental education contains methods, tasks and principles. The model is implemented in several stages and reflects the principles of interaction between educators and students. The final result of the implementation of the model is an increase in the level of intellectual development of preschool children. A set of intellectual tasks for improving emotional and logical intelligence is also described. We draw attention to the fact that the emotional perception of educational games increases (with sthenic emotions) and decreases (with asthenic emotions) the receptivity of the material.
Developmental education includes: intellectual games “Mind Games” (board and dynamic); “What, where, when?”, “Intellectual musical game”, “Help the fairy-tale hero” (depending on the purpose of the lesson); “Spanish Dance”, “Riddles of Aunt Owl”, etc.
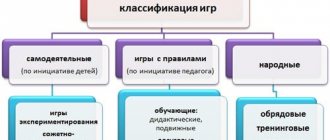
Rice. 1. Model of intellectual education of preschool children through developmental education in the MBDOU “Child Development Center - Kindergarten No. 162” in the city of Voronezh
The result of the implementation of the model is an increase in the level of intellectual education of preschool children.
The monitoring showed the following results: in the vast majority of children, average indicators of the development of cognitive processes prevailed in percentage terms. The most difficult things for children to do are intellectual games and tasks. Not all children have a specific idea of the world around them, and therefore, for example, sorting animals and birds according to their affiliation is difficult for many. The level of verbal and logical thinking remains below average in 15% of children. The concentration of auditory and visual attention is above average. Most children have above-average ideas and imagination. This is explained by age-related characteristics, since children with age more often play role-playing games that require creative imagination and critical thinking. Memory is also above average, but what matters here is the emotional appeal of what needs to be remembered and retained.
Thus, the effectiveness of developmental education, which contributes to the intellectual education of preschool children, has been substantiated. The development of cognitive motivation is influenced by the emotional appeal of teaching aids, games, and training sessions.
The developed pedagogical conditions for developmental education contribute to the intellectual education of preschool children.
Literature:
- Yaretskaya A. Yu. Work program of the educational discipline “Developmental game in the activities of preschoolers” of the educational program of professional retraining “Pedagogical activities in preschool education”: educational method. materials / A. Yu. Yaretskaya. - Voronezh, 2016. (ANOO VO "ISO"). — 16 s.
Specifics of the learning process for preschoolers
Definition 1
Learning is the process of transferring knowledge and developing skills, stimulating the activation of cognitive and research activities, associated with the assimilation of a system of scientific knowledge and the acquisition of practical skills in various fields of activity, the development of creative abilities, the assimilation of cultural norms and moral principles of activity, aesthetic views and moral principles.
The learning process is a structural component of the pedagogical process. It is associated with the activities of the teacher in transferring knowledge and skills to students, and with their activities in obtaining, assimilating and practical application of this knowledge and skills.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
The learning process has its own characteristics depending on the age stage of the child’s development.
Education in a preschool educational institution differs in content, methods and forms of organization. All knowledge and skills at this age are transferred to the child by adults. He guides the child’s cognition, guides the development and retention of educational material, and helps to put the acquired data into practice.
In preschool age, children's education has the following specifics:
- The main activity of preschoolers is play. Therefore, the learning process takes place in a playful way;
- The learning process has a systematic structure: there are no scientific theories and concepts in it, children receive basic ideas about the structure of nature and society, and receive simple practical skills in various fields and areas of activity;
- The emergence of difficulties in cognition associated with the separation of significant objects from secondary ones;
- The importance of visually presenting objects and cognitive processes to children;
- The need to develop motivation for cognitive activity;
- The importance of approval, praise, encouragement of children for their success in learning and the elimination of punishment for lagging behind;
- Inability to concentrate on objects for a long time, poor performance and frequent mood swings;
- The need for accessibility of teaching information, its simplicity and clarity of construction;
- A high degree of development of the emotional component, which prevails over other types of activity;
- Application of effective and figurative methods in cognition.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work The essence of the learning process for preschool children 410 ₽ Abstract The essence of the learning process for preschool children 230 ₽ Examination The essence of the learning process for preschool children 240 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
What principles is the theory of developmental education for preschool children based on?
1. The goal of education is the development in the child of figurative forms of knowledge of the world - visual-imaginative thinking and creative imagination as the most characteristic of the preschool period of childhood (A.V. Zaporozhets), cognitive activity and curiosity, emotional and sensory experience.
2. Inclusion in the content of training of a rich picture of the world and elementary concepts about the surrounding reality. The picture of the world is made up of ideas about people, their relationships, the world of objects and work activities, nature and art. Children can master elementary concepts about the surrounding reality, presented in figurative form - system knowledge, N.N. Poddyakov, V.I. Loginova) and various methods of cognition (sensory analysis, experimentation, construction and use of visual models, etc.).
3. The organization of educational and cognitive activity is based on the child’s solution of a wide range of problem-game tasks (educational games, problem-game situations, creative tasks) , encouraging the child to take the position of a subject of activity. The child’s creative abilities are intensively developed in children’s experimentation - this is an activity in which the child acts as a kind of researcher, independently influencing various objects or objects with the aim of knowing them.
4. The teacher organizes cooperation between children, using both direct and indirect methods: “provoking actions”, joint resolution of problem situations, creating an environment of psychological comfort, positive assessment of achievements, methods of pedagogical support aimed at helping a child experiencing certain difficulties, removing he is under emotional stress.
5. Features of interaction of preschool children in educational and cognitive activities:
— Joint-individual cooperation, where the connection is expressed as a “goal-result” (in the process of modeling, appliqué, manual labor, decorative drawing)
— Joint-sequential cooperation - the adoption of a common goal, the sequential execution of actions by the participants (like a “conveyor”), which requires mutual regulation. It is carried out on the basis of a problem situation that requires the interaction of children (in the process of educational situations of mathematical, environmental, speech development; for example, retelling by episodes, creative storytelling by roles, etc.)
— Joint-interacting cooperation – work in pairs and micro-groups, interaction between them in the process of creating a common product of activity.
6. The result of developmental education is the child’s ability to independently solve accessible cognitive problems, the ability to consciously use different methods and techniques of cognition, interest in experimentation, readiness for logical cognition, and the ability for educational and cognitive cooperation with adults and peers.
What is the theory of the gradual formation of mental actions (P.Ya. Galperin, N.F. Talyzina) ?
This theory is significant for organizing the education of preschoolers, since learning, as a rule, begins with subject perception.
An action, before becoming mental, generalized and abbreviated, goes through a number of stages. Let's look at these stages using the example of children mastering sensory standards of form.
1. Stage of acquaintance with a new action - the indicative basis of the action is revealed to the child. “How to distinguish a circle and a square? (presence - absence of corners)"
2. The stage of performing an action in a material form - the action is performed in external form with the deployment of all the operations included in it (Roll: “it rolls - it doesn’t roll”).
3. The stage of formation of the action as external speech - all elements of the action are presented in external speech, the action is developed, not generalized. “What do you need to do to find out which of the figures is a circle and which is a square? Ride it."
4. The stage of forming an action in external speech to oneself - the action is performed silently, like saying “to oneself.” “Remember what you need to do to find out the shape of a geometric figure.”
5. The stage of action formation in inner speech - the action is internalized. “Which shape do you think this is - a circle or a square?”
Next, the child only needs a quick glance at the geometric shapes to determine their shape.