What is morality
The spiritual heritage of humanity contains a colossal store of knowledge, skills, ways of thinking and communication, systems of moral and legal norms.
The concept of morality implies a system of internal spiritual qualities, norms and rules that determine a person’s behavior, his attitude towards himself and others.
A person with high morality demonstrates independence and will, self-control and willingness to bear responsibility, the ability to empathize and help others. In its highest manifestations, morality is realized in acts of selfless service, dedication and even self-sacrifice.
With a low level of morality, a person gives priority to satisfying immediate personal interests. He is prone to moral uncertainty and is influenced by populist and relativistic ethical systems. Prefers to follow the path of least resistance, choosing solutions that do not require excessive spiritual and physical costs. He demonstrates indifference and indifference towards others.
What is moral education - definition
Moral and civic education
In cadet schools and patriotic gardens, morality is considered together with citizenship. This is especially true in our time, when there are class and civil wars, when the history of military battles from different eras is deliberately distorted.
Moral and patriotic education is expressed in informing about the political and social needs of the country and developing the ability to defend one’s opinion. Then the child will be able to adequately assess the situation in his state, understand its problems and make conscious decisions to protect the interests of his Fatherland: for example, transfer some of his things and toys to an orphanage, keep his yard clean, be attentive and careful in relation to suspicious persons (fraudsters, drug dealers), etc.
The task of civic education is to teach children to accept their country with all its advantages and disadvantages, not to exchange it for foreign countries, but to solve problems on their own. Also, this process is intended to subsequently push older schoolchildren to choose a profession that will help not only personal development, but also partially contribute to solving government problems.
The concept of moral education
Modern Russian society finds itself at the epicenter of moral and ethical problems.
The processes of globalization and universalization affect the culture of the country, the destruction of traditional national spiritual values occurs, as a result of this, social evil increases, as well as moral mistrust of each other intensifies, interpersonal and interethnic conflicts are perceived as a common occurrence, empathy disappears, a tendency is established to destroy national cultural traditions, the ideals of young people are reoriented from spiritual to material. The question of the ethical dimension of the negative consequences of imposing elements of Western living standards on our society remains relevant, which further aggravates the crisis of spirituality in Russian society. This can be seen in the devaluation of morality and moral imperatives, as well as in the absence of humane attitudes at the level of interpersonal relationships, thanks to which the full development of personality occurs.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
Russian society, more than ever, requires the presence of a socially valuable and spiritually stable personality, a “moral person” with a high level of culture, capable of becoming a responsible, active, active subject of social development.
Among researchers there is no definition of the concept of “moral education”; they characterize it as:
- complex integrated process;
- the process of formation of moral qualities, character traits, skills and habits of behavior;
- a social phenomenon that obeys the laws of social development;
- purposeful influence of the older generation on the younger generation in order to develop stable moral qualities in them;
- a purposeful process of organizing and stimulating diverse activities and communication, aimed at mastering a moral culture of behavior and attitude towards the surrounding world;
- a process whose specific functions are carried out according to its own rules and patterns;
- the core of harmonious personality development;
- the form of transformation of experience and the sphere of implementation of human moral culture;
- development of skills and abilities of moral behavior, formation of humane relationships.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Moral education - goals, features, methods 480 ₽ Abstract Moral education - goals, features, methods 280 ₽ Test work Moral education - goals, features, methods 250 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Brief conclusions
It is better to start nurturing moral character and moral behavior from preschool age. Results can be achieved faster with the cooperation of teachers and parents. Children need to not only explain moral rules, principles and norms, but also demonstrate them in practice by their example.
The moral education of schoolchildren further determines the moral character of the country's citizens. If teachers focus the attention of their students on the social problems of the state (Nazism, racism, fascism, selfishness and indifference), teach them to solve difficulties in all possible ways, and not look for excuses, then the number of proactive strong individuals in the state will increase who will change the future for the better.
The problem of morality of junior schoolchildren
The moral education of schoolchildren in primary school is based on the authority of the teacher. His personal qualities and behavior are copied by children unconsciously. Primary school is an important period in the development of a child’s moral personality. In communist times, the morning began with a collective meeting, where positive and negative moments from the life of the school were discussed. The whole day was built on collective events and extracurricular conversations designed to foster a harmoniously developed personality.
Nowadays, any discussion of a student’s misconduct is perceived as humiliation of the individual. Parents immediately file complaints with the Ministry of Education and the prosecutor's office, without delving into the situation. Teachers began to consider the moral education of younger schoolchildren superficially. That is, in their subjects, teachers have practically stopped teaching about moral feelings towards the Motherland, faith, people, themselves, nature, work, and animals. Various problematic situations are resolved at the highest level (director - parents), while the influence of fathers and mothers can differ radically from pedagogical requirements.
How to form the foundations of moral thinking
The concept of moral thinking implies the process of assimilation and comprehension of moral rules and facts, their analysis and evaluation with the subsequent development of moral decisions.
Moral thinking presupposes the ability to compare one's actions with their consequences for others. The basis of its development is the child’s ability to be sensitive towards others, the ability to sympathize. In the first stages, these qualities are laid down by the example of an attentive and sensitive attitude of parents to the needs of the baby. He finds understanding, which then grows into mutual understanding. A friendly atmosphere creates positive patterns of interaction with others. The child demonstrates positive actions towards others, since he himself has experience of positive perception of their use towards him. Such a child does not shy away from people and does not show indifference.
Methodological foundations of moral education
The ability to remember about others is a necessary condition for developing the ability to think about the consequences of one’s steps and the willingness to bear responsibility. As the child develops, these qualities are formed and reinforced through constant and patient explanation of the admissibility or, conversely, unacceptability of certain actions.
Tip: Discuss cartoon and movie characters together. Ask questions - let the child learn to express his opinion and form moral value judgments.
Actively comment on life situations that your child has witnessed. Explain your actions and decisions, especially when it comes to choosing between your own well-being and the need to do the “right thing”. Don't avoid discussions if your child expresses an opinion different from yours. Reason, give examples from books, from films, from life. Do not hesitate to accept the child's point of view if his arguments are fair.
Extracurricular activities - visiting the library as a method of education
Moral and environmental education
Spiritual and moral education is inseparable from the flora and fauna. After all, kids unconsciously reach out to our smaller brothers. Therefore, educational institutions organize corners of nature where children are taught to look after and care for fish, hamsters, rabbits, birds, and plants.
It is important to instill in children a love for all living things, to reinforce a sense of responsibility for our little brothers, and to show that environmental pollution can lead to global irreversible consequences. Daily observations of natural phenomena, plants, and animal behavior broadens a child’s horizons and emotional experiences.
Moral education of primary schoolchildren and preschoolers through environmental methods allows them to develop altruism, attentiveness, caring, mutual assistance, patience, kindness, hard work, and responsibility. It is important for teachers to constantly draw a parallel between the sensations of animals and plants with the feelings of people.
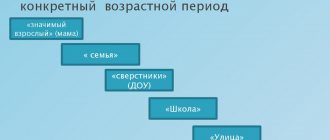
School period
The next stage is associated with the beginning of schooling. The student gets acquainted with new systems of rules and correlates them with the rules of the family. The first doubts visit him, the sense of justice becomes sharper. He gains his first experience in defending the right to his own opinion, his own scale of values. At this time, the child needs support. Parents must strengthen him in his beliefs and prevent him from plunging into a state of moral uncertainty. In turn, the child is ready to turn to his parents for help; they remain the main authorities.
Lessons at school necessarily contain a moral aspect
After ten to twelve years, teenagers begin to recognize themselves as part of not only the family and school community, but also a new generation.
Peer authority increases. Their behavior patterns are of increasing interest. There is a process of adopting new value systems and assessing their acceptability. The stage of hesitation and search begins. A teenager develops a need for abstract judgments about justice and moral values. Now the task of parents is to move from authoritarian leadership to the position of an empathetic adviser involved in the child’s problems. Behavior control is still necessary, but its forms should not create a lack of mutual trust and the emergence of barriers to communication.
Directions of moral development of schoolchildren
Advice: At all stages, a very important task of parents is to create an atmosphere of mutual care and trust in the home. Try to avoid sorting things out in front of the child. Try to join forces.