LEGO - design and robotics in preschool educational institutions.
LEGO - design and robotics in preschool educational institutions.
Currently, new games and entertainment have appeared in the education system of preschool children. Children easily master information and communication technologies, and it is difficult to surprise them with traditional visual means. The development of the educational process goes in many directions, affecting mainly the formation of the personal qualities of a preschooler. The result of the educational activities of preschool educational institutions today is considered not the sum of knowledge, skills and abilities, but the personal qualities acquired by the child: curiosity, activity, independence, responsibility and good manners.
We, teachers, strive to use a variety of techniques and methods, realizing that we ourselves must learn modern technologies, because our students live in a world of computers, the Internet, electronics and automation. They want to see this in educational activities, to study, use, understand. One of these modern methods is considered to be joint (preschoolers, teachers and parents) integration activity - Lego construction.
Every child is a born designer, inventor and researcher. These tasks inherent in nature are especially quickly realized and improved in constructive activities. Construction is a very interesting and exciting activity; it is closely connected with the intellectual development of a child.
This type of activity is distinguished by its novelty in the use of Lego, a construction set with which the child has the opportunity to communicate, explore and play.
The construction set helps children bring their ideas to life, build and imagine, working with passion and seeing the end result. Lego encourages both your head and your hands to work equally. Lego is always a new discovery, a new idea. A new impetus for development.
Children who are interested in design are distinguished by rich fantasy and imagination, an active desire for creative activity, a desire to experiment and invent; They have developed spatial, logical, mathematical, associative thinking, memory, and this is the basis of the child’s intellectual development.
Construction is closely related to the sensory and intellectual development of a preschooler. It is of particular importance for improving visual acuity, accuracy of color perception, tactile qualities, development of small muscles of the hands, perception of the shape and size of an object, space. Children try to establish what an object is like and how it differs from others; master the ability to measure the width, length, height of objects; begin to solve constructive problems “by eye”; develop imaginative thinking; learn to imagine objects in different spatial positions, mentally change their relative positions. In the course of classes, work is being done on the development of the intellect of imagination, fine motor skills, creative inclinations, the development of dialogic and monologue speech, and the expansion of vocabulary. Particular attention is paid to the development of logical and spatial thinking. Pupils learn to work with the proposed instructions, develop the ability to cooperate with a partner and work in a team.
MAGAZINE Preschooler.RF
Lego construction in kindergartenLego is the most popular game on the planet. The word Lego has two meanings: “I learn” and “I build . The British Toy Traders Association awarded the designer the title of “Toy of the Century” . Here is the characteristic that the world's best designer corresponds to:
- Unlimited game potential.
- Suitable for girls and boys.
- Suitable for all ages.
- Suitable for any season.
- Healthy and calm games.
- You can play for a long time.
- Develops imagination and creativity.
- The more Lego bricks, the better.
- The quality is visible in every detail.
The Lego constructor can be divided into two large classes: classic small Lego and large Lego Duplo.
Lego Duplo is intended for children from one and a half years old. There isn't a lot of variety in these sets - mostly rectangular and square bricks and plates. Many of the cars in this set come apart into two parts - a platform with wheels and the body of the car. Many sets have doors, windows, and fences.
Such elements greatly enliven the construction. Also, one of the advantages of these sets is the abundance of plastic men and animals that are attached to the plate. In addition, Lego Duplo has many educational sets designed to teach a child counting, the ability to build according to instructions, and letters.
Small Lego.
Lego Creator. It’s best to start introducing your child to classic small Lego with sets in this series. It contains a lot of thematic sets with all kinds of houses, cars, lighthouses, castles, and just boxes with cubes, windows with doors and tiles.
Lego City. There are only city-themed sets available here (police stations, fire departments, ambulances, trains, etc.)
Thematic sets. Lego tried to collect all the most popular hobbies of children in their thematic sets. There are series based on individual films and cartoons, all kinds of robots, transformer monsters, ninjas and spaceships.
Lego Ruckers are sets for assembling cars that have inertia mechanisms.
Lego Technician. These are very interesting and very complex kits, where models are assembled mainly not from bricks, but from all kinds of bushings, gears and sticks. Thanks to this, all models have moving, mechanized parts and give a good idea of how levers, pistons, gears work, and how machines work from the inside.
Lego Mindstroms. This is a multifunctional kit containing many sensors and programmable chips. Using it, you can assemble real robots and, most importantly, determine their behavior and create programs in a special programming language.
The themes of LEGO games are vast. We build cities, ships, look for treasures, and dramatize popular Russian folk tales. We enrich our vocabulary, expand our horizons, and discover the unknown. We actively combine gaming and educational activities.
The approach to learning does not cause hostility, the material is absorbed more easily, and the load on the body is reduced.
Children are tireless designers; they learn to design “step by step,” which improves their visual and figurative thinking.
Activities with Lego help children realize their ideas, build, fantasize, work enthusiastically and see the end result. All activities with Lego take place in the favorite “build and play” game form.
Light construction classes develop fine motor skills, imagination and logic. Composing a single object from construction blocks is a difficult but feasible task. An experienced teacher guides children along the path from simple to complex. During the Lego construction class, problems of a problematic nature are collectively solved, which affects the development of search activity; children are not afraid of mistakes, they know how to analyze them and with particular pleasure look for different ways to solve the same problem. At the end of each lesson, the finished design is played out in a plot.
Watching children aged 4-5 years making light constructions, I saw that playing with them was monotonous. All the children’s buildings were limited to the construction of turrets (who can build the highest) or simply piling parts on top of each other like a wall. Children could not combine familiar elements in a new way; creativity did not manifest themselves in the game. Playing with Lego was accompanied by low speech activity, both in explaining the planning and execution of the construction, and during the game, the vocabulary was poor, and the children did not voice their actions in the game. The plan was not completed, fine motor skills of the hands were poorly developed, many tried to forcefully press the parts in order to find the correct position for fastening, or resorted to rough fastening options: hitting them with a fist or palm.
All this encouraged me to study more deeply the methods of light construction for use in various fields.
After analyzing the observations, I determined the purpose of my further work.
Goal: to promote the development of technical creativity in preschool children, to provide them with the opportunity for creative self-realization through mastering LEGO construction.
Objectives: to form coherent speech, the ability to consistently and logically construct a speech utterance, enrichment of subject and verb vocabulary; to form a sustainable interest in constructive activities, the desire to create, invent; develop imagination, constructive imagination and the ability to creatively use acquired skills and create an attractive play situation that encourages children to develop their own ideas; cultivate friendly relationships, develop independence when working with schemes.
She also determined the expected result: during the work on light-duty construction, the child should know: the main details of the light-duty constructor (purpose, features); the simplest fundamentals of mechanics (stability of the structure, strength of the connection, types of connection of parts); name the details of a Lego constructor; technological sequence of manufacturing simple structures. Be able to: select the parts necessary for design (by type and color); design, focusing on a step-by-step scheme for manufacturing structures, according to a sample; work in pairs and in a small group of children; comment on actions with Lego elements, follow verbal instructions; use diagrams of a future building completed by LEGO.
In order for the work to bring greater results, I introduced parents to the importance of light construction in the lives of children and, most importantly, the importance of joint play between children and parents. Already at an early age, parents purchase beautiful games and toys for their children, including LEGO construction sets. But no matter how good they are, they cannot bring the benefit that can be obtained from them if mom or dad are not nearby. After all, even such a spectacular constructor as LEGO cannot replace parents for a child. While playing with LEGO together with parents, the child does not feel lonely, relationships are formed and strengthened, and a sense of self-confidence develops. In a playful form, children can more easily automate sounds, broaden their horizons, and expand their vocabulary. And during the workshop meeting, the parents themselves played the role of creators. Using the diagram to write a story about a future building, they shared their idea, and after construction, the diagram helped them write a story about playing with Lego buildings. I was glad that the parents did not have any difficulties in this, because they are the ones who are a model of competent speech for the child and an incentive to increase speech activity. At this meeting, we decided to diversify and replenish the Lego constructors by purchasing Lego DUPLO sets.
For successful work, I planned a long-term plan for light construction, including it in educational activities, in independent activities, in didactic games, not forgetting to use it in various educational areas. We organized exhibitions for parents “Miracle Christmas Tree” , putting all the emotions into the work after the New Year's party, helped return animals to the zoo after a trip to Africa, made buildings for pets and their homes, shared our experience of building LEGO crafts and playing with them with younger children groups, learned to lay out beautiful patterns from Lego pieces using a model and solve simple examples. And funny Lego men helped us get acquainted with the characteristics of sounds, find their place in a word and help us learn to read. With Lego, it is easier for us to remember numbers and letters, laying them out according to a pattern and later from memory.
At the end of the middle group, children freely used words from the vocabulary in their speech, taking into account the size of the parts (names of the parts, supplemented them with definitions (Green medium brick, red cube)) were able to build elementary buildings according to a creative plan, according to a model. Not everyone has developed the ability to build according to a diagram due to insufficient attention span. It was more difficult for some children to write a story about their work, but we continued to work on this in the older group. I think that the difficulty in this arose due to age-related speech impairments, since not all children are able to At this age they mastered the system of their native language.Working in pairs took place in a calmer environment, the children learned to negotiate with each other and share details while working.
How to play Lego.
For many, like me, Lego is associated with construction according to instructions. Until the age of 8-12, a child is unlikely to build according to instructions. That is, if he wants and is interested, then please. But if he is indifferent to the amazing buildings that Lego designers offer, then that’s great too. During this period, the development of creativity and imagination is much more important than the development of spatial thinking (which is activated when assembling according to instructions).
Adults and children must play without instructions, making structures on the fly. Lego is very similar to clay or plasticine - you can make anything, crush it into a ball and make something completely different.
However, once you buy a new set, you should definitely assemble it according to the instructions. For what? To see and understand all the possibilities of the parts. Pay attention to the strength of the building, show how to lay bricks crosswise, how to press the parts so that they fit tightly and how to separate them (without using teeth).
Lego is creativity and it’s good when it’s free from templates and samples!
Practical part.
Offer a small identical Lego set. (3 cubes, 3 bricks). Ask to build a duck (without a sample) without peeking at each other. As a result of one task, all the ducks are different. This is the creative imagination of every person. If someone modeled an inverted duck (that is, with the cube buttons down and the tubes up), then this person has unconventional thinking.
Conclusion: each child has his own vision of the world, an imagination that needs to be developed.
Make up your own story.
Divide into creative groups. Offer construction sets and plates. Give a task: a few words. You need to come up with and build a story with these words. For example: words (cat, bridge, fear). Parents model a story with these words. For example:
“Once upon a time there was a cat. One day he climbed onto a high bridge and became very scared. Rescuers arrived and removed him from the bridge.
The next group has a different story. Stories can be united by one character.
At the end of the master class on Lego construction, we decided: to develop the creative abilities and design skills of children, to educate individuals who are able to independently set problems for themselves and solve them, finding original ways to solve them.
| Next > |
Robots Education Creativity
Details Published: 09.12.2018 10:50
Lightweight construction and the basics of robotics today are the most popular areas of development for children, and it doesn’t matter at all whether they are schoolchildren or preschoolers. Teachers search for lesson plans on the Internet or create their own innovative programs. Today we would like to introduce you to one of these programs.
It was sent by Narmina Azimovna Azimetova from the Tyumen region, teacher, MBDOU d/s “Sibiryachok”. The program is designed for children 3-4 years old.
Club activities program
"LEGO construction"
It's easier to do everything with LEGO,
It's easier to get smarter with LEGO.
LEGO is the most popular board game on the planet. The word “LEGO” has two meanings in Latin: “I learn” and “I add.” The British Toy Traders Association awarded LEGO the title of “Toy of the Century.”
The introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education involves the development of new educational models, which should be based on educational technologies that comply with the principles:
- developmental education;
- scientific validity and practical applicability;
- compliance with the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency;
- unity of educational, developmental and training goals and objectives of the education process for preschool children;
- integration of educational areas;
- solving program educational problems in joint activities and independent activities of adults and children;
- accounting for the preschooler’s leading activity—games.
LEGO is one of the most famous and widespread pedagogical systems, widely using three-dimensional models of the real world and a subject-based gaming environment for the learning and development of a child. Play is the most important companion of childhood. LEGO allows children to learn through play and learn through play.
During educational activities, children become builders, architects and creators; while playing, they bring their ideas to life. Starting with simple figures (from 3 to 5 years), the child moves further and further. Seeing his successes, he becomes more confident and moves on to the next, more complex stage of training.
The prospects for using LEGO technology are determined by the high educational opportunities that are required of these tools at the present stage: multifunctionality, technological and aesthetic characteristics, use in various play and educational areas. Paramonova L.A. believes that even the smallest set of building elements opens up a new world for the child. A child does not consume, he creates, creates objects, the world and life.
Games with construction sets help develop children's creative and intellectual abilities, design skills, imagination, and the ability to foresee the results of their actions.
Children begin to solve difficult problems through fun, creative play. Preschoolers develop fine motor skills and improve their speech quality. LEGO construction contributes to the sensory development of a preschooler, because Bright, functional details can affect literally all the child’s senses:
visual acuity, accuracy of color perception, tactile qualities, perception of shape, size of an object, space and much more are improved.
Building with LEGO helps a child see the world in all its colors. The brighter, more holistic, and more emotional children’s impressions of the world around them are, the more interesting and varied the buildings will become.
Tasks:
- Learn to see the design of an object, analyze its main parts, their functional purpose.
- Develop a sense of symmetry and aesthetic color schemes of buildings.
- To develop preschoolers' interest in modeling and design, to stimulate children's scientific and technical creativity.
- Improve children's communication skills when working in pairs, teams, and sharing responsibilities.
- Strengthen children's knowledge about the world around them.
- To identify gifted, talented children with unconventional creative thinking and abilities in constructive activities and to ensure further development.
LEGO construction is included in the regulations for the educational activities of the kindergarten and is implemented within the educational area “Cognition”, section “Design”, implemented by the preschool educational institution program of the L.A. Center. Wenger "Development+". The content of educational activities in LEGO construction is based on the methodological developments of L.G. Komarova. “We build with LEGO.”
Using the LEGO constructor, educational tasks with preschoolers are solved in the following areas:
- Development of fine motor skills of the hands, stimulating general speech development and mental abilities in the future.
- Learning to correctly and quickly navigate in space.
- Obtaining mathematical knowledge about counting, shape, proportion, symmetry.
- Expanding your ideas about the world around you - about architecture, transport, landscape.
- Development of attention, ability to concentrate, memory, thinking.
- Teaching imagination and creative thinking.
- Mastering the ability to mentally divide an object into its component parts and assemble a whole from the parts.
- Learning to communicate with each other, respecting one’s own and others’ work.
LEGO construction begins at the age of three: children in the second junior groups are offered the LEGODUPLO construction set. Children get acquainted with the basic details of the construction set, methods of fastening bricks, and children develop the ability to correlate the results of their own actions in constructing an object with a model.
In the middle group (from 4 to 5 years old), children consolidate the skills of working with LEGO constructors acquired in the younger group and get acquainted with the small LEGODASTA constructor for the first time. The last four classes are held with him. The predominant form of work is design by design. Children experiment freely with building materials. The sample may be shown at the beginning of the lesson and then removed. The organization of educational activities is built in individual and subgroup forms of work with children, the requirements of SanPin are met.
LEGO construction sets provide a great opportunity for a child to learn through experience.
LEGO games help develop intellectual qualities: attention, memory, especially visual; the ability to find dependencies and patterns, classify and systematize material; the ability to combine, that is, the ability to create new combinations from existing elements and parts; ability to find errors and shortcomings; spatial and imaginary; the ability to foresee the results of one's actions.
Most LEGO games are not limited to the proposed tasks, but allow children to create new versions of the task, that is, engage in creative activities.
Unbeknownst to the child, these games help to acquire a very important skill - to restrain yourself, not to interfere with each other, to think and make decisions, not to ask for help if you haven’t tried to do it yourself.
Program content
Middle group
- Acquaintance with new details of the Lego Duplo constructor, consolidation of knowledge about those already known to children.
- Teach children to create a plot composition on a board.
- Continue to teach how to build according to your own plans.
- Learn to plan your work, be able to tell.
- Continue to introduce children to the concept of stability of a building, its strength.
- Teach children to analyze a building from a picture and identify its main structural parts.
- Continue to teach how to work in a team, learn how to build a joint building, and plan the stages of its creation.
- Learn to convey the shape of an object using Legos, select parts according to shape, size and stability in accordance with the content.
- Learn to follow the teacher's instructions.
- Give the concept of symmetry.
- Continue to teach children to work according to the example.
- Continue to develop the ability to navigate in space (on a plane), to use words denoting spatial relationships.
- Continue to introduce children to different ways of fastening Lego pieces.
- Continue introducing children to Lego mosaics, teach them to distinguish geometric shapes, their color location in space.
- Learn to distinguish geometric shapes regardless of their color and location, learn to combine shapes by color and shape.
- Give children the opportunity to experiment with Legos.
Form for presenting the result: Technology of design skills, creative thinking in middle-aged preschoolers using LEGO construction.
— search and research methods that stimulate the cognitive activity of students;
— experimental research, design and research activities that develop the creative initiative of students;
- activity-based types of practical tasks that involve a creative approach.
Taking into account the age and physiological characteristics of the development of children of middle preschool age, in this program a large place is given to conducting classes in the form of a game.
In the process of working with Lego constructors, various forms of tasks were used:
- according to the model;
- on cards with models;
- according to one's own design;
- the teacher gives the task, the children complete it;
- tasks are formulated by the child and carried out by the children and the teacher;
- children give each other tasks;
- The task is given by the teacher and carried out by the parents and the child.
To successfully carry out activities with Lego constructors, certain conditions were created:
- free access to the construction set is organized so that children can choose the parts they need;
- children were thoroughly introduced to the sample;
- specially selected music to accompany productive activities;
- the safety of the building is ensured for some time.
TO THE LEVEL OF CHILDREN'S PREPARATION
| Vospi- tannik must | Basic program | Component preschool educational institution | Regional component |
| Know | Have an idea of architecture, know who architects are and what they do. Understand what an algorithm, rhythm, rhythmic pattern is. The symbol for an algorithm is a notation. Generalized ideas about the objects being constructed (bridges: railway, pedestrian; buildings: residential, schools, theaters | Be able to distinguish and name the parts of a Lego constructor (Lego Duplo, Lego Dacta) Understand what symmetry is and be able to alternate colors in your buildings. | Our country, its main city Moscow and with the help of a Lego set can easily be used to convey the defensive structures of Russian cities (Kremlin walls, wooden and stone ancient Russian architecture, churches, bell towers and other architectural objects) |
| Be able to | Be able to distinguish and name the parts of a Lego constructor (Lego Duplo, Lego Dacta) Can mentally change the spatial position of an object and its parts. Design according to the conditions set by adults and the plot of the game. Master generalized methods of design (combinatorics, objectification, removing unnecessary things, etc.) Independently and creatively implement your own design ideas from different materials. Design according to a given scheme and build the scheme of the future design itself. Be able to mentally change the spatial position of a constructed object, its parts, details, and imagine what position they will occupy after the change. Be able to analyze the operating conditions of a future structure, establish the sequence of their implementation and, based on this, create an image of the object (a bridge across a river for pedestrians of a certain width) Be able to build and implement your own plan (selecting a topic, creating a plan for future design, selecting materials and design methods) Be able to work in a team and in pairs. Be able to place a building on a board and build collective buildings. Be able to talk about your construction. Be able to follow the teacher's instructions Be able to create a plot composition on the board. | Fasten Lego parts in a variety of ways. Be able to distinguish geometric shapes, their color, shape, location in space (mosaic) Distinguish geometric shapes regardless of their color and location, be able to combine shapes by color and shape. Be able to convey the characteristic features of fairy-tale characters using the Lego Duplo (Dakta) constructor Be able to use Lego buildings in theatrical games and role-playing games. Create moving structures and find simple technical solutions. | Participate in the development of projects on local history topics. Use Lego to convey the appearance features of animals and birds in the Moscow region. Be able to model human figures, fairy-tale heroes in various Russian costumes. Model folk holiday entertainment (carousels, swings, bear fun) |
Working with Lego parts stimulates and develops the potential creative abilities of every child, teaches him to create and destroy, which is also very important. Destroy not aggressively, not thoughtlessly, but to ensure the possibility of creating something new.
By breaking his own Lego building, the child has the opportunity to create another one or complete some of its parts from the freed parts, acting as a creator. Thus, Lego construction is a type of modeling creative and productive activity. With its help, difficult learning tasks can be solved through fun, creative games.
Each child is unique, and each is born with abilities that can and should be developed. Preschool children have a great desire to create and get results. By creating the necessary conditions for constructive activity, we help the child to understand the world around him and realize his place in this world.
| Designer type | Ascertaining stage |
| Builder | 12 groups |
| Lego | 11 groups |
| Mechanical constructor | 4 groups |
| Large modules | 3 groups |
| Volumetric puzzles | 4 groups |
| Magnetic mosaic | 4 groups |
| Paper constructor | 5 groups |
| Fun slides | 3 groups |
Observing children's social role-playing games
Goal: Identify the use of different constructors in gaming activities. Ascertaining stage.
Children unite their crafts with one theme. They design according to ideas; graphic diagrams, samples in pictures, photographs, and technological maps are not used. Therefore, the designs of objects are not sufficiently appropriate for the age of children.
The final stage
All children began to use construction sets in their free activities.
Children often design based on ideas; they also use samples in pictures, photographs, and technological maps. Children's crafts have become more perfect and more expressive, which indicates acquired design skills.
The level of children’s knowledge acquisition can be determined using the criteria I developed for assessing children’s mastery of Lego construction and the development of their creativity.
The analysis is carried out twice a year at the beginning of the school year and at the end according to three criteria:
● Knowledge acquired
● Knowledge is not specific, gets confused, makes mistakes
● Knowledge not acquired
The child’s activities are also assessed at each lesson.
As a result of the first year of classes in the circle, the children learned well:
- recognize the details of the LEGO constructor, depicted from 3 different positions (straight, on top, on the side),
- recognize and correctly reproduce structures using development diagrams,
- create graphic models of structures based on analysis of a specific sample,
- The level of development of children's imagination has increased.
A worse result was obtained when completing the task “Constructing an object according to plan.” During the construction process, not all children were able to retain the idea and implement the design in accordance with the plan. The designs of the objects were not age appropriate (they were simple in execution).
By studying in a circle, children will acquire work culture skills: they will learn to maintain order in the workplace, distribute time and effort when making models (each lesson has its own topic) and, therefore, plan activities.
In addition, design is closely related to the sensory and intellectual development of the child: visual acuity, perception of color, shape, size are improved, and mental processes (analysis, classification) are successfully developed.
LEGO construction helps preschoolers enter the world of social experience. Children develop a unified and holistic idea of the objective and social world. The lesson plan includes topics such as “Animals”, “Urban and rural buildings”, “Furniture”, “Toys”, “Such different transport”, “Ships”, “Journey to a fairy tale” and others. On calendar holidays, thematic exhibitions will be organized in the children's creativity corner, where we will present the works of children attending additional classes in LEGO construction
PLAN FOR WORKING WITH CHILDREN
2 YOUNGER GROUPS
| № | Classes | Quantity classes |
| 1. | Safety precautions in LEGO construction classes. | 1 |
| 2. | Spontaneous individual LEGO - children's play, or acquaintance with LEGO continues. | 1 |
| 3. | Brick Explorers. Game "Colorful Towers". | 1 |
| 4. | Magic molds. Game "What's Hidden?" | 1 |
| 5. | Games “Magic Color”, “Dreamers”. | 1 |
| 6. | Let's get acquainted with the form LEGO bricks. | 1 |
| 7. | Game "Guess my model" | 1 |
| 8. | Magic bricks. Construction of a common fence. | 1 |
| 9. | We build magic stairs. | 1 |
| 10. | Game "Beautiful Houses". | 1 |
| 11. | Mold Researchers. On-board simulation. Flower for mom. | 1 |
| 12. | Pets. - dog. - cat. | 2 |
| 13. | Wild animals of hot countries: - giraffe. | 1 |
| 14. | Construction of different trees. | 1 |
| 15. | Transport construction: - airplane - car (based on sample) - ship | 3 |
| 16. | Furniture for a doll: - table - chair - sofa - bed. | 2 |
| 17. | We are building a bird. | 1 |
| 18. | Project work: “Children’s playground.” | 2 |
Annual planning of design classes in the middle group
| month | a week | Lesson number | Title of the lesson | Program content |
| September | 3,4 | Diagnostics | ||
| October | 1 | 1 | "Fences" | I. Design according to a model and transform it according to conditions. to train children in closing space by arranging planar figures; in distinguishing and correctly naming primary colors (red, blue, yellow, green) and geometric shapes (square, triangle, circle, rectangle); consolidate ideas about the details of the designer; teach to understand an adult, think, find your own solutions. |
| 3 | 2 | "Gate and Fence" | Learn to build gates for a fence; carefully and tightly fasten the parts of the Duplo lego set; exercise children in constructing buildings according to the model and transforming them according to given conditions; in distinguishing and correctly naming primary colors, geometric shapes and familiar construction parts; clarify children’s ideas about the relative size of objects using the example of a gate (lower - higher, narrower - wider); practice the skill of accurately connecting building parts, placing them on top of each other and placing them next to each other; teach children to analyze buildings; consolidate the ability to close space, giving it a certain shape. | |
| november | 1 | 3 | "Furniture for dolls" | Develop the ability to identify their functional parts in real objects; continue to introduce children to the concept of design; learn to analyze a sample; teach children to work with construction sets; design various pieces of furniture; unite your buildings with a single plot; teach how to create a building, correlating its size with the size of the toy; encourage the creation of new versions of already familiar buildings; form an idea of geometric shapes, develop spatial thinking. |
| 3 | 4 | "House" | Learn to build a big house for a farmer; develop imagination and creativity; learn to finish what you start; to form a generalized idea of houses, that they are different (single- and multi-story); arouse in children an emotional attitude towards the building; exercise children in fencing small spaces with cubes, bricks and plates installed vertically and horizontally; practice the ability to make floors; in mastering spatial concepts (in front, behind, below, above, left, right); practice converting buildings into length and width; develop independence in finding design methods; cultivate perseverance and accuracy during work, mutual understanding and mutual assistance. | |
| December | 1 | 5 | "Garage for cars" | teach children to prepare the base for the ceiling, to navigate the plane; build a building in accordance with the size of the toys; practice comparing objects by length, height, width; teach children to work together, agreeing on a work plan. |
| 3 | 6 | "Multi-storey building" | to form generalized knowledge about buildings; establish a relationship: the more floors, the higher the house; learn to build according to a drawing, select building materials independently; promote the development of search activity, encourage children to look for ways to transform buildings (in height, length, width, adjusting with suitable details); exercise in mastering spatial concepts (in front, behind, below, above, left, right); in the practical mastery of the correlation of buildings by size (height, length, width). | |
| January | 1 | 7 | "Truck" | Learn to build a familiar structure using a graphic model, correlate its elements with parts of an object; continue to learn to examine a sample, identify parts, determine their spatial location (behind, in front, on top, on, etc.), develop the ability to perceive an object holistically; introduce a new part - a cylinder, give an idea of its properties (in comparison with a block); encourage the transformation of the structure by introducing additional details into it. |
| 3 | 8 | "Train" | Introduce techniques for connecting bricks with wheels, with each other, and with the main parts of the train; develop fantasy and imagination; clarify children’s ideas about the details of the construction set and their properties; exercise in design, analysis of samples, and transformation of structures according to given conditions; continue to develop the ability to correlate elements of a graphic model with parts of a structure, develop the ability to reflect one’s observations and knowledge about objects in buildings. | |
| February | 1 | 9 | "Ships and boats" | Give a general idea of ships; teach design methods; learn to combine parts in shape and color in construction, establish the spatial arrangement of buildings; continue to introduce children to the details of the construction set, practice replacing some parts with others; teach children to discuss, analyze designs, plan their construction with their partner; encourage individuals to independently find individual ways to solve the problem associated with transforming the building. |
| 3 | 10 | "Streets of our city" | II. Design according to conditions. Continue introducing traffic lights; learn traffic rules; build a roadway and an overpass; activate children’s knowledge, the ability to creatively apply previously acquired constructive skills; learn to place your buildings on a certain site; develop the ability to work in a team. | |
| March | 1 | 11 | "Bridge for pedestrians" | Learn to build a bridge, accurately connect building parts, and place them on top of each other; give an idea of bridges, their purpose, introduce different types of bridges (pedestrian, transport), with the elements of their structures (descents, steps, supports, floors); teach children to build simple bridges; develop the ability to examine a sample, make the building stable, practice comparing objects by size (long - short); stimulate children's creativity and independence, promote their speech and play communication. |
| 3 | 12 | "Bridges for Transport" | consolidate an understanding of the different types of bridges, their purpose, structure; continue to introduce elements of their structures (descents, supports, floors); practice building bridges; develop the ability to create structures according to given conditions; develop the ability to analyze examples of buildings and illustrations; practice comparing objects by size (wide - narrow); develop the ability to independently select the necessary details by size, shape, color, and combine them. | |
| April | 1 | 13 | III. Design by design. consolidate the acquired knowledge and constructive skills in children; promote the development of their creativity, independence and organization; teach children to think about the topic of a future building in advance (create a plan) and implement it, achieving their goal. Teach to compare the resulting building with the intended one. | |
| 3 | 14 | consolidate the acquired knowledge and constructive skills in children; promote the development of their creativity, independence and organization; teach children to think about the topic of a future building in advance (create a plan) and implement it, achieving their goal. Teach to compare the resulting building with the intended one. | ||
| May | 1,2 | Diagnostics |
- TV, VCR, stereo system.
- Posters, diagrams, dummies, books, illustrative material, photographs, toys, balls, etc.
| № | Author | Book title, publisher, the year of publishing |
| 1. | Komarova L.G. | “Building with Legos” “LINK-PRESS” Moscow 2001 |
| 2. | LussT.V. | “Formation of skills in constructive play activities in children with the help of Legos” Humanitarian Publishing Center VLADOS Moscow 2003 |
| 3. | Institute of New Technologies | Game aids LOGO-Verlag Moscow Institute of New Technologies |
| 4. | Feshina E.V. | LEGO construction in kindergarten. |
| 5. | Author: L.S. Kiseleva, T.A. Danilina, T.S. Lagoda, M.B. Zuikova. – 2nd ed., rev. and additional - arr. | “Project method in the activities of a preschool institution” Arkti Publishing House Moscow 2004 |
| 6. | them. A.V. Zaporozhets | Basic development program for a preschool child Publishing house "Karapuz" Moscow 1997 |
| 7. | A.N. Davidchuk | “Development of constructive creativity in preschool children” Moscow “Enlightenment” 1976 |
| 8. | Edited by M.A. Vasilyeva, V.V. Gerbovaya, T.S. Komarova | Kindergarten education and training program Moscow Mosaic-Synthesis 2005 |
| 9. | Z.V. Lishtvan | Construction Moscow "Enlightenment" 1981 |
| 10. | L.A. Paramonova | Children's creative construction Publishing house "Karapuz" Moscow 1999 |
| 11. | A.N. Davidchuk | Development of constructive creativity in preschoolers Moscow "Enlightenment" 1976 |
Master class “LEGO construction in kindergarten”
Olga Vladimirovna Kaygorodova
Master class “LEGO construction in kindergarten”
Slide 1. Good afternoon, dear colleagues. Today in our master class we will plunge into the world of LEGO. I would like to talk about LEGO construction and share my experience in organizing children's activities using LEGO constructors.
Slide 2 . Question from the audience: “Look at the picture on the screen, tell me what do children like to do?”
That's right...children love to play. Children all over the world can communicate in one language – the language of play. It is play that helps them understand the complex, diverse world in which they grow and develop. In various games, children activate their natural abilities - imagination, dexterity, emotions, feelings, intelligence, communication, etc. Children play with everything that comes into their hands.
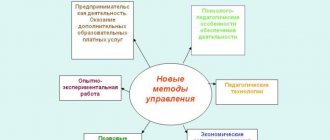
Slide 3. In connection with the introduction of Federal State Educational Standards into the preschool education system, teachers have great opportunities to use new pedagogical technologies, methods, and various types of didactic material. The most popular equipment today is considered to be LEGO materials, which include various types of construction sets.
In pedagogy, Lego technology is interesting because, being built on integrated principles, it combines elements of play and experimentation.
Question from the audience: “Now let’s try together to give a short description of this unique designer?”
Slide 4.
1. Security.
2. Wide gaming possibilities.
3. Benefit. Develops imagination, creativity, logical thinking.
4. Availability of a large number of different series.
5. Versatility. Suitable for all ages: girls and boys and even adults.
6. Easy assembly and disassembly of structures.
7. This is an opportunity for a group game.
Slide 5. Educational areas in preschool educational institutions do not exist in a “pure form”. Their integration always occurs. Through the use of Lego constructors, you can effectively solve educational problems implemented in kindergarten.
Today I will try to introduce you to some of the options for using legoconstruction in various educational fields.
Slide 6. Social and communicative development.
In my opinion, one of the main goals of Lego building is to teach children to work effectively together. LEGO allows you to: create joint buildings, united by one idea, one project. Using this technology, the ability to collaborate with a partner and work in a team is formed. The ability to set goals, initiative, the ability to get things done, the desire to defend one’s ideas, leadership, and breadth of interests develop.
Slide 7. Cognitive development.
In the process of LEGO construction, preschoolers develop mathematical abilities and form sensory representations: children, by counting parts, blocks, fasteners, calculating the required number of parts, their shape, color, length, reinforce the concepts: “high - low”, “wide - narrow”. Children become familiar with such spatial indicators as symmetry and asymmetry and orient themselves in space. In GCD of an educational nature, LEGO is used in experimental activities as the material from which the construction set is made (“What is it made of?”, “Find the same one.”)
Slide 8. Speech development.
By training our fingers, we have a powerful impact on the performance of the cerebral cortex, and, consequently, on the development of speech. In the process of constructing from Lego, children communicate, negotiate, reason, learn to defend their point of view, while their vocabulary expands, the ability to ask questions, and dialogical and monologue speech develop.
We also use LEGO in the process of preparing for literacy training (we suggest creating an image of a letter from LEGO bricks; building various objects that begin with the specified sound.
Retelling the story not according to the plot picture, but according to the three-dimensional image of the scenery from the construction set, helps the child understand the plot, which makes the retelling detailed and logical. The children and I tell familiar fairy tales and create our own fairy tales and stories, constructing plots from LEGO.
Slide 9 . Artistic and aesthetic development.
LEGO - the designer comes to the rescue when preparing for a children's theater production. First, children create their own characters from a construction set, and then voice them.
Slide 10. Physical development.
Parts of a large LEGO construction set can be used as equipment for physical education classes.
• walking/running like a snake between construction parts
• shuttle run
• maintaining balance
• exercises to develop coordination of movements
• exercises to develop flexibility, speed and agility.
For corrective gymnastics and prevention of flat feet, you can use LEGO mats. These rugs will massage the feet due to the convex shape of the LEGO parts, and will also attract children with their brightness due to a variety of colors.
Slide 11. As we found out earlier, LEGO construction sets are distinguished by their versatility. Suitable for all ages: girls and boys and even adults.
With children aged 3–4 years, LEGO sets with large elements and simple connections of parts are used.
Slide 12. With children 4–5 years old, the design becomes more complicated, medium-sized elements are used, and more complex options for connecting parts are used. In the middle group, color photos and pictures with images of models are used, according to which children must build. Creative activity is carried out according to a theme, a model, a plan and the simplest conditions.
Slide 13. At 6–7 years old, various types of LEGO construction sets are offered for technical creativity, from large ones with simple connections of elements to the most miniature ones with complex execution techniques. When working with older preschoolers, you can use tasks in the form of graphic diagrams, complicated models of future buildings, work based on design, conditions, and various thematic tasks.
Slide 15. Forms of implementation of the LEGO method in kindergarten.
• Planned lessons (10–15 minutes in the junior group, 20 minutes in the middle group, 25–30 minutes in the senior and preparatory groups).
• Individual work of a teacher in pairs with a child or with a subgroup of children (once a week for no more than 40 minutes) - preparing the child for the competition; working with gifted or underdeveloped children.
• Long-term and short-term projects, the participants of which can be: teacher, children and parents.
• Everyday independent construction, construction games in free time from scheduled classes.
• Festivals, competitions, quizzes.
• Club work, which is carried out by teachers of a preschool institution.
Slide 16. LEGO - a game - is the most important companion of childhood, allowing children to learn while playing. Every LEGO building is a fantastic new adventure, always different, always fun, educational and rewarding.